If there is one thing that the recent shake-up in the employment market has brought home to many, especially those in tech, it is that work as traditionally understood by many of previous generations, can be unstable. Late in 2023 TikTok’s parent company, ByteDance, dismissed about 1,000 employees in its gaming unit. Fortnite developer Epic Games parted ways with over 800 personnel and Unity has continued a spree that started in 2023 and runs into 2024. The estimates for 2023 are 9000 people impacted in the gaming entertainment sector alone.
I always find a look at layoffs.fyi kind of interesting, they have been around a couple of years now with data going back to 2020. Frontdesk, Invision, Twitch, Lazada, Citrix, Audible, Flipkart Trend Micro, Unity, New Work SE, Google. Some of the numbers are substantial. As of today, 51 Tech companies and 7528 known layoffs in 2024 alone.
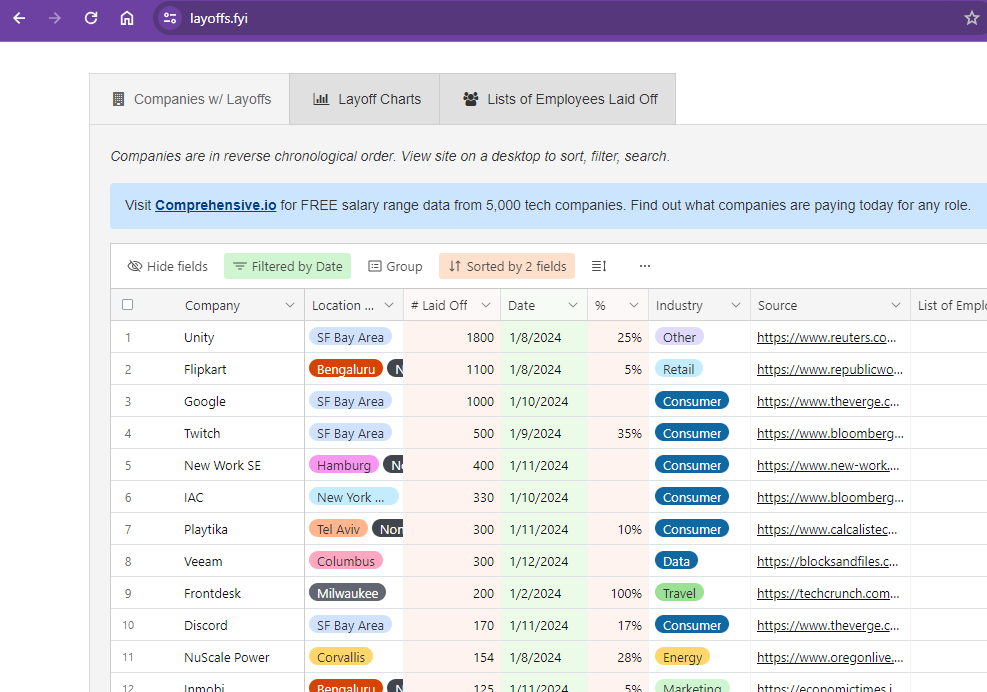
The recent changes in the employment market have highlighted the instability of traditional work structures. This has been particularly evident in the tech industry but it is not isolated to tech.
Several factors contribute to this shift:
- High job openings: Despite a slight decrease in November, job openings in the US remain high by historical standards. This indicates a strong demand for workers.
- Job market resilience: The US economy added more jobs than expected, demonstrating the resilience in the labor market.
- Inflation and interest rates: The Federal Reserve has raised its benchmark interest rate multiple times to combat inflation, which has led to a gradual decline in job openings since peaking in March 2022. This could potentially lead to a cooling of the job market. In Europe, inflation dogged many European countries in 2022 and 2023 falling to 3.1% in the EU and 4.7% in the UK
- Occupational Shift: occupational mixes shifted, with the most highly skilled individuals enjoying the strongest job growth over the last decade, while middle-skill workers had fewer opportunities.
- Geographic Concentration: Employment growth in general has been concentrated in a handful of regions.
- Labor Mobility: Labor mobility in the EU has been rising as workers in the lower-income regions migrate to dynamic cities to fill jobs.
- COVID-19 Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in national employment rates for 23 of the EU Member States in 2020 compared with the previous year. In the US, the COVID-19 pandemic led to significant job losses, but many of these jobs have since been restored.
- Fake Work: According to Fortune, some companies reportedly hired people simply to snub competitors and neutralize the likelihood of those valued resources being snatched up by them. What they described as also being “thanks to an over-hiring spree to satisfy the “vanity” of bosses at the likes of Meta and Alphabet“.
These factors all lead to a reevaluation of traditional employment models, with many individuals and companies now exploring more flexible and resilient alternatives. This includes remote work, contract-based roles, and a greater emphasis on skills rather than specific job titles.
It’s a complex issue with many facets, and the job market will evolve in response to these and other pressures.
Organizations, much like living organisms, undergo cycles of growth and contraction influenced by economic conditions. During economic upturns, companies often seize expansion opportunities, hiring more talent to meet increased demands.
This growth phase can lead to a sense of abundance and optimism within the workforce. Conversely, economic downturns may prompt organizations to reassess their structures, resulting in layoffs, restructuring, or a more streamlined approach to operations.
Individual contributors must recognize these patterns to better navigate the shifts in their work environments. Understanding that these changes are often not personal but strategic responses to economic realities can provide a valuable perspective. By staying attuned to the broader organizational context, individuals can position themselves to adapt and contribute effectively during periods of change.
People-to-Manager Ratio
The people-to-manager ratio is a critical aspect of organizational dynamics. This ratio influences the effectiveness of management and the well-being of individual contributors. While there’s no universal formula for the perfect ratio, finding the right balance is essential.
In scenarios where the ratio is too high, individual contributors may feel a lack of guidance or support, leading to burnout and diminished performance. On the other hand, an excessively low ratio might result in micromanagement and hinder autonomy.
Organizations that strike the right balance empower managers to provide meaningful support to their teams while ensuring that individual contributors have the autonomy and resources needed to excel in their roles. This balance fosters a healthy work environment where everyone can thrive.
Imposter Syndrome
Imposter syndrome is a common challenge that individual contributors, especially very competent younger people, and women in particular, may face. This is prevalent, particularly during times of organizational change. It involves persistent feelings of inadequacy and a fear of being exposed as a fraud, despite evidence of competence or clear qualification.
To overcome imposter syndrome, one should actively reflect on achievements, skills, and the unique perspectives one brings to the role. Seeking constructive feedback from colleagues and mentors can provide valuable insights into one’s strengths. Acknowledging accomplishments, no matter how small helps build confidence and dispel the irrational belief of being an imposter. Watch out for gaslighters though.
In the face of organizational shifts, individuals need to recognize their intrinsic value. Understanding that you were hired for a reason and have the skills to contribute meaningfully can be a powerful antidote to any imposter syndrome you may suffer from.
Professional Growth
Regular self-assessment is a cornerstone of professional growth.
Individual contributors should evaluate their roles in the broader organizational context, considering how their work aligns with overarching goals. This involves a critical examination of tasks, responsibilities, and the impact of their contributions.
An effective self-evaluation goes beyond job responsibilities; it delves into the quality of work, initiative, and the ability to collaborate with colleagues. By identifying areas for improvement and actively seeking growth opportunities, individuals position themselves as proactive contributors to the organization’s success.
This reflective process allows individuals to align their goals with the organization’s objectives, ensuring that their contributions remain relevant and valuable, even in the face of organizational changes.
Reinvention of the self
In times of uncertainty, like now, the ability to reinvent oneself becomes a strategic advantage. This reinvention can take various forms, including acquiring new knowledge, adapting behaviors to meet evolving challenges, and delivering tangible results.
Continuous learning is another cornerstone of professional development. If we end up with more than four cornerstones, consider that the building that is your occupation, career, and role, may not be a quadrilateral.
We should all actively seek opportunities to acquire new skills, stay informed about industry trends, and engage in relevant training programs. This not only enhances individual capabilities but also contributes to the organization’s overall resilience.
Adapting behaviors involves staying attuned to evolving workplace dynamics. This may include embracing collaborative technologies, refining communication skills, and fostering a mindset of adaptability. Being open to change and displaying a positive attitude can position you as an asset during times of organizational flux.
Delivering tangible results is also a fundamental aspect of proving one’s value. Individual contributors should focus on outcomes, highlighting achievements and the positive impact of work. This may involve setting measurable goals, taking ownership of projects, and consistently delivering high-quality results that contribute to the organization’s success.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a catalyst for innovation and problem-solving. Those who cultivate such a skill can navigate uncertainties with agility. During periods of organizational change, critical thinking involves strategic analysis, identifying potential challenges, and proposing effective solutions.
Proactive engagement in critical thinking demonstrates leadership qualities. Individual contributors should actively participate in discussions, offer insights, and contribute to decision-making processes. This not only showcases value but positions one as an essential contributor to the organization’s resilience and adaptability.
Critical thinking involves anticipating future trends and challenges. By staying ahead of the curve, you can position yourself as a more valuable asset, contributing to the organization’s ability to navigate changing economic climates.
Good luck otherwise with the current storm that we seem to be sailing through and hope for calmer waters soon, but hopefully not so calm that you get bored.
